Limb Transplant
- Home
- Limb Transplant
Limb Transplant
Limb Transplant, also known as Vascularized Composite Allotransplantation (VCA) or Hand/Arm Transplant, is a highly complex surgical procedure where a donor limb (usually a hand or arm, and in rare cases, a leg) is transplanted onto a recipient who has lost a limb due to trauma, disease, or congenital conditions. This involves not just the transplantation of bones and muscles, but also blood vessels, nerves, tendons, and skin.
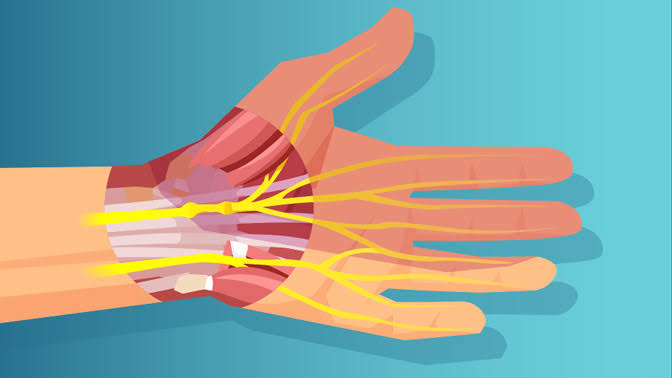
Key Aspects of Limb Transplant
Eligibility for Limb Transplant:
– Patients who have lost a limb due to trauma, infection, or certain diseases like cancer.
– Individuals with a strong psychological resilience, as limb transplants involve lifelong commitment to medication and rehabilitation.
– Cases where prosthetics are not a suitable or sufficient solution.Procedure Details:
– Donor Selection: A matching donor is required, who has similar limb size, skin tone, and blood type to reduce the risk of rejection.
– Microsurgical Techniques: Surgeons connect the bones, tendons, muscles, blood vessels, and nerves of the donor limb to the recipient’s corresponding structures.
– Revascularization: Restoring blood flow to the transplanted limb is crucial for the survival of the transplanted tissues.
– Nerve Regrowth: Nerve reconnection allows for sensation and movement in the transplanted limb, but nerve regeneration is a slow process, and full functionality might take years.Recovery and Rehabilitation:
– Intensive Physical Therapy: Post-surgery, patients undergo intensive physical therapy to regain movement, strength, and fine motor skills.
– Occupational Therapy: Helps patients relearn how to perform daily activities using the transplanted limb.
– Sensory Rehabilitation: Nerve function returns slowly, and patients may experience gradual improvements in sensation over months to years.Immunosuppressive Therapy:
– Lifelong Immunosuppression: To prevent the body from rejecting the transplanted limb, patients must take immunosuppressive medications for life.
– Risk of Rejection: Even with immunosuppressants, there is always a risk that the body will reject the transplant. Rejection can be acute (happening soon after surgery) or chronic (developing over time).Risks and Complications:
– Infection: Both at the transplant site and systemically, due to immunosuppressive medications.
– Graft Rejection: The immune system may recognize the transplanted limb as foreign and attack it, leading to partial or full loss of the limb.
– Side Effects of Medications: Long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs can cause serious side effects, including increased risk of infections, cancer, and kidney damage.
– Psychological Challenges: Patients may struggle with the emotional and psychological impact of adapting to a new limb.Long-term Outlook:
– With advanced surgical techniques and immunosuppressive protocols, many patients experience a good level of functionality in the transplanted limb.
– Patients often regain motor control and sensory perception, though it varies depending on how quickly nerves regenerate and how well the transplant integrates.Ethical Considerations:
– Limb transplants raise ethical questions about the quality of life improvements versus the risks of lifelong immunosuppression and the potential for rejection.
– Finding suitable donors is also a challenge, as limbs must be donated after death, and the consent process can be sensitive for families of donors.Limb Transplant vs. Prosthetics:
– Advantages of Limb Transplant:
– Potential for more natural movement and sensation compared to prosthetics.
– Aesthetically, transplanted limbs look more like natural limbs.Disadvantages:
– Requires lifelong immunosuppression.
– Risk of rejection and complications from surgery.
– Longer recovery and rehabilitation time compared to getting prosthetic limbs.Successful Cases:
Some limb transplants have led to remarkable results, with patients regaining the ability to perform everyday tasks such as writing, holding objects, and even playing sports.Future Directions:
– Research is ongoing in areas such as reducing the need for immunosuppressive drugs, improving surgical techniques, and possibly growing limbs in the lab using stem cells and tissue engineering.
Our Focused Specialties
Multi-Specialty Care Hub
Discover India’s diverse multi-specialty health departments and treatments. We’re dedicated to ensuring a healthier tomorrow, navigating the dynamic realm of Indian healthcare. Our wide range of specialties includes top-notch hospitals, selected based on quality and healthcare facilities. Join us for a personalized journey to optimal health and wellness.
Gastro-intestine
Pulmonology
Ophthalmology
Gynaecology
Nephrology
Cardiac
Hematology

Neurology
Bone & Joint
Looking for an expert !
Our Healthcare is home to some of the eminent doctors in the world

Dr Rajesh Sharma

Dr Sandeep Vaishya

Dr Sandeep Vaishya

Dr Rajesh Sharma

Dr Rajesh Sharma

Dr Sandeep Vaishya
Easy Access Links
- International Patients
- We & Why
- Core Specialites
- Common Procedures
- Hospitals
- Doctors
- Treatment Locations
- Way To Healing
- Wise to ask before
- Comfort and Satisfaction
