Urology (Urinary Tract Specialty)
- Home
- Urology (Urinary Tract Specialty)
Urology (Urinary Tract Specialty)
Urology is a medical specialty focused on diagnosing and treating disorders of the urinary tract and male reproductive system, including kidney stones, urinary infections, prostate issues, and bladder control. In India, the urology specialty offers advanced treatments, including minimally invasive surgeries, robotic-assisted procedures, and affordable healthcare options. With skilled urologists and latest technology, patients benefit from early detection, effective treatment, and improved quality of life at cost-effective rates. Medkins Healthcare makes accessing expert Urology in India easy by connecting you with leading urologist doctors and hospitals and supporting you throughout your treatment process.
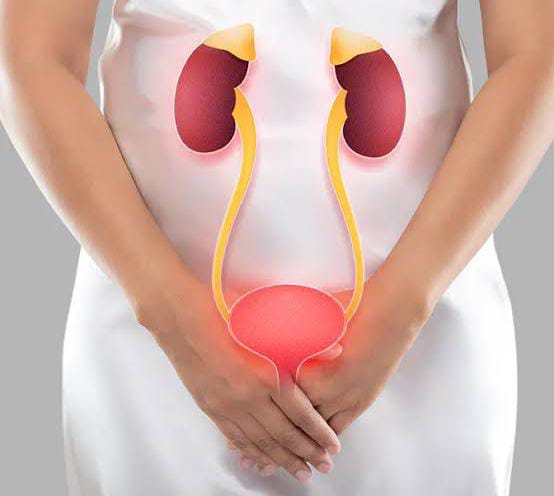
Diseases Treated in Urology
Kidney Stones (Nephrolithiasis) – Hard mineral and salt deposits that form in the kidneys. They can cause severe pain, especially when passing through the urinary tract. Stones vary in size, and large stones may require surgical removal or non-invasive treatment like shock wave therapy.
Bladder Cancer – Cancer that begins in the cells of the bladder’s lining. Symptoms include blood in the urine, frequent urination, and pelvic pain. It is more common in smokers and those exposed to certain chemicals.
Prostate Cancer – A common cancer in men that originates in the prostate gland. Prostate cancer often grows slowly but can spread to other areas of the body if untreated. Symptoms include difficulty urinating, blood in the urine, and pelvic pain.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) – A non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland, common in older men. BPH can obstruct the flow of urine, causing frequent urination, weak urinary stream, and incomplete bladder emptying.
Testicular Cancer – Cancer that develops in the testicles, the male reproductive glands. It is rare but most common in younger men (ages 15-35). Symptoms include a lump in the testicle, swelling, or discomfort in the scrotum.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) – Infections that occur anywhere along the urinary tract, including the bladder, kidneys, ureters, and urethra. Symptoms include frequent urination, burning sensation while urinating, and cloudy urine. In severe cases, it can spread to the kidneys.
Erectile Dysfunction (ED) – The inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse. Causes can include vascular issues, neurological conditions, psychological factors, or hormonal imbalances.
Bladder Stones – Hard masses of minerals that form in the bladder, often as a result of incomplete bladder emptying. They can cause lower abdominal pain, frequent urination, and blood in the urine.
Interstitial Cystitis (Painful Bladder Syndrome) – A chronic condition causing bladder pressure, pain, and frequent, urgent urination. It is more common in women and may be associated with pelvic floor dysfunction.
Hydronephrosis – Swelling of the kidney due to a buildup of urine caused by a blockage in the urinary tract or by kidney stones, tumors, or an enlarged prostate.
Varicocele – An enlargement of the veins within the scrotum, similar to varicose veins. It can lead to pain, swelling, and even infertility.
Overactive Bladder (OAB) – A condition in which the bladder muscle contracts involuntarily, leading to frequent and urgent urination. In some cases, it can cause incontinence.
Urinary Incontinence – Involuntary leakage of urine. There are several types, including stress incontinence (due to pressure on the bladder), urge incontinence (strong need to urinate), and overflow incontinence (bladder doesn’t empty completely).
Penile Cancer – A rare cancer that occurs on the skin or within the penis. Symptoms include a growth or sore on the penis that doesn’t heal.
Phimosis – A condition where the foreskin cannot be fully retracted over the glans of the penis, which can cause discomfort, difficulty urinating, and increased risk of infection.
Paraphimosis – A medical emergency where the retracted foreskin of an uncircumcised male cannot be returned to its normal position, leading to pain and swelling.
Peyronie’s Disease – A condition where fibrous scar tissue develops inside the penis, causing curved, painful erections. It may lead to erectile dysfunction or difficulty with intercourse.
Urethral Stricture – A narrowing of the urethra due to injury, infection, or inflammation. This can cause difficulty urinating, pain, and a weak urine stream.
Conditions Managed and Treated in Urology
Male Infertility – Urologists treat male infertility caused by various conditions like varicocele, hormonal imbalances, blockages in the reproductive tract, or low sperm count.
Urinary Retention – The inability to empty the bladder completely or at all. Causes include an enlarged prostate (BPH), nerve damage, or blockages in the urethra or bladder.
Hematuria (Blood in the Urine) – The presence of blood in the urine, which can indicate a variety of conditions including UTIs, kidney stones, bladder cancer, or trauma to the urinary tract.
Nocturia – Frequent nighttime urination, often linked to bladder dysfunction, prostate issues, or kidney disease. It can significantly disrupt sleep.
Neurogenic Bladder – A condition where nerve damage affects normal bladder control, leading to incontinence or retention. It is often caused by spinal cord injuries, multiple sclerosis, or diabetes.
Ureteropelvic Junction (UPJ) Obstruction – A blockage at the junction where the kidney connects to the ureter, leading to reduced kidney function and hydronephrosis.
Vesicoureteral Reflux (VUR) – A condition in which urine flows backward from the bladder into the ureters or kidneys. It can lead to recurrent UTIs and kidney damage.
Priapism – A prolonged and often painful erection that lasts for hours and is not related to sexual activity. It requires emergency treatment to prevent permanent damage.
Urinary Fistulas – Abnormal connections between the urinary tract and other organs (e.g., the bladder and the bowel), leading to the leakage of urine.
Urinary Obstruction – Any blockage that prevents the normal flow of urine through the urinary tract, often caused by stones, tumors, or an enlarged prostate.
Bladder Dysfunction due to Diabetes – Diabetes can cause nerve damage affecting the bladder, leading to conditions like neurogenic bladder, urinary retention, or incontinence.
Hydrocele – A fluid-filled sac around the testicle that causes swelling in the scrotum. It is generally painless but can grow large and uncomfortable.
Undescended Testicles (Cryptorchidism) – A condition where one or both testicles fail to descend into the scrotum at birth. It can affect fertility and increase the risk of testicular cancer if not corrected.
Urological Procedures & Surgeries
Cystoscopy – A diagnostic procedure where a thin tube with a camera (cystoscope) is inserted into the urethra to examine the bladder and urethra. It helps in diagnosing bladder cancer, UTIs, and bladder stones.
Ureteroscopy – Similar to a cystoscopy, but this procedure uses a small scope to examine the ureters and kidneys. It is often used to diagnose and treat kidney stones or blockages in the ureters.
Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) – A surgical procedure used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). The surgeon removes parts of the prostate that are blocking urine flow using a resectoscope inserted through the urethra.
Prostate Biopsy – A procedure where small samples of prostate tissue are removed and examined for cancer. It is typically done using a needle guided by ultrasound through the rectum or the perineum.
Lithotripsy (Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy – ESWL) – A non-invasive procedure that uses shock waves to break up kidney stones into smaller fragments that can be passed through the urine.
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL) – A minimally invasive procedure to remove large kidney stones. A small incision is made in the back, and a nephroscope is used to break and remove the stones.
Urethral Dilation – A procedure to treat urethral strictures (narrowing of the urethra). Dilators are inserted into the urethra to stretch it, allowing easier urine flow.
Vasectomy – A permanent form of male contraception, where the vas deferens (the tubes that carry sperm) are cut or sealed to prevent sperm from entering the semen.
Vasectomy Reversal – A procedure to restore fertility in men who have previously undergone a vasectomy. The vas deferens are reconnected to allow sperm to be present in the semen again.
Prostatectomy – A surgical procedure to remove part or all of the prostate gland. It is often done for prostate cancer or severe cases of BPH. Techniques include open surgery, laparoscopic, or robotic-assisted surgery.
Nephrectomy – Surgical removal of a kidney. It can be done for kidney cancer, severe kidney damage, or as a part of kidney donation. It can be performed as an open or laparoscopic procedure.
Pyeloplasty – A reconstructive surgery to repair a blockage or narrowing of the ureteropelvic junction (UPJ). This helps restore normal urine flow from the kidney to the bladder.
Penile Implants – A surgical procedure to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) that doesn’t respond to medication. A device is implanted into the penis to allow a man to achieve an erection.
Circumcision – The surgical removal of the foreskin from the penis. It may be performed for medical, cultural, or religious reasons, and can treat conditions like phimosis or balanitis.
Hydrocelectomy
– Surgical removal of a hydrocele, which is a fluid-filled sac surrounding a testicle. This procedure is performed to relieve pain, discomfort, and swelling in the scrotum.Bladder Sling Surgery
– A procedure used to treat stress urinary incontinence, primarily in women. A sling is placed around the urethra to support it and prevent urine leakage.Artificial Urinary Sphincter (AUS) Implantation
– A surgical treatment for severe urinary incontinence, often after prostate surgery. An artificial sphincter is implanted around the urethra to control urine flow.Radical Cystectomy
– Surgical removal of the bladder, typically to treat advanced bladder cancer. The procedure may include removing nearby organs, such as the prostate or uterus, and creating a urinary diversion, such as an ileal conduit.Ureteral Stent Placement
– Insertion of a small tube (stent) into the ureter to ensure proper urine flow from the kidney to the bladder. This is often done after stone removal or to relieve blockages caused by tumors or strictures.Bladder Augmentation
– Reconstructive surgery to enlarge the bladder, often performed to treat bladder dysfunction or reduce bladder pressure caused by conditions like neurogenic bladder.Sling Procedures for Male Incontinence
– A surgery to treat male stress urinary incontinence, typically following prostate surgery. A sling is placed to support the urethra and reduce urinary leakage.Penile Fracture Repair
– Emergency surgery to repair a penile fracture, which involves a tear in the tunica albuginea (the layer surrounding the erectile tissue), often caused by trauma during intercourse.Sperm Retrieval Techniques
– Procedures such as Testicular Sperm Extraction (TESE) or Microsurgical Epididymal Sperm Aspiration (MESA) are used to extract sperm in men with obstructive azoospermia, where blockages prevent sperm from being present in the semen.Retrograde Pyelogram
– A diagnostic procedure where contrast dye is injected into the ureters through the bladder, and X-rays are taken to identify blockages, tumors, or abnormalities in the urinary tract.Fulguration
– A procedure that uses electrical energy or a laser to remove or destroy abnormal tissue, commonly used for bladder tumors or lesions.Urethroplasty
– A surgical repair or reconstruction of the urethra, commonly performed to treat urethral strictures or trauma.Orchiectomy
– The surgical removal of one or both testicles, often performed to treat testicular cancer or as part of hormone therapy for prostate cancer.Intravesical Therapy
– A treatment where medication is directly instilled into the bladder through a catheter to target bladder cancer cells.Renal Artery Angioplasty and Stenting
– A procedure to widen narrowed arteries supplying the kidneys using a balloon catheter, often followed by placing a stent to keep the artery open. It is used to treat renal artery stenosis, which can lead to hypertension and kidney damage.Artificial Urinary Bladder Construction (Neobladder)
– A procedure in which a new bladder is constructed using a portion of the intestine after bladder removal (due to cancer). The neobladder allows patients to pass urine more naturally.
Our Focused Specialties
Multi-Specialty Care Hub
Discover India’s diverse multi-specialty health departments and treatments. We’re dedicated to ensuring a healthier tomorrow, navigating the dynamic realm of Indian healthcare. Our wide range of specialties includes top-notch hospitals, selected based on quality and healthcare facilities. Join us for a personalized journey to optimal health and wellness.
Gastro-intestine
Pulmonology
Ophthalmology
Gynaecology
Nephrology
Cardiac
Hematology

Neurology
Bone & Joint
Looking for an expert !
Our Healthcare is home to some of the eminent doctors in the world

Dr Rajesh Sharma

Dr Sandeep Vaishya

Dr Sandeep Vaishya

Dr Rajesh Sharma

Dr Rajesh Sharma

Dr Sandeep Vaishya
Easy Access Links
- International Patients
- We & Why
- Core Specialites
- Common Procedures
- Hospitals
- Doctors
- Treatment Locations
- Way To Healing
- Wise to ask before
- Comfort and Satisfaction
